1. Mida la resistencia del devanado del motor.
Configure el multímetro en el rango Ω (ohmios) y mida la resistencia de cada uno de los devanados trifásicos (U, V, W).
En circunstancias normales, las resistencias de cada fase deben ser similares y estar dentro del rango de referencia del fabricante (por ejemplo, 2,6 Ω, 0,7 Ω, 0 Ω correspondientes a diferentes rangos de velocidad).
2. Verifique la resistencia del aislamiento.
Utilice el rango de resistencia de aislamiento del multímetro (o un megaóhmetro) para medir la resistencia de aislamiento de cada fase al Motor del ventilador carcasa.
La resistencia de aislamiento debe ser superior a 1 MΩ; un valor inferior a este puede indicar envejecimiento del aislamiento o absorción de humedad.
3. Verifique el capacitor de arranque del motor (si lo hubiera)
Configure el multímetro en el rango de medición de capacitancia y mida si el valor de capacitancia del capacitor de arranque coincide con el valor nominal (por ejemplo, 10 µF).
Un condensador defectuoso provocará dificultades para arrancar el motor o un aumento del ruido.
4. Verifique el voltaje de la fuente de alimentación.
Mientras el motor del ventilador está funcionando, use un multímetro para medir el voltaje entre fases y el voltaje entre fases y tierra para asegurarse de que cumplan con el voltaje nominal (por ejemplo, 220 V/380 V).
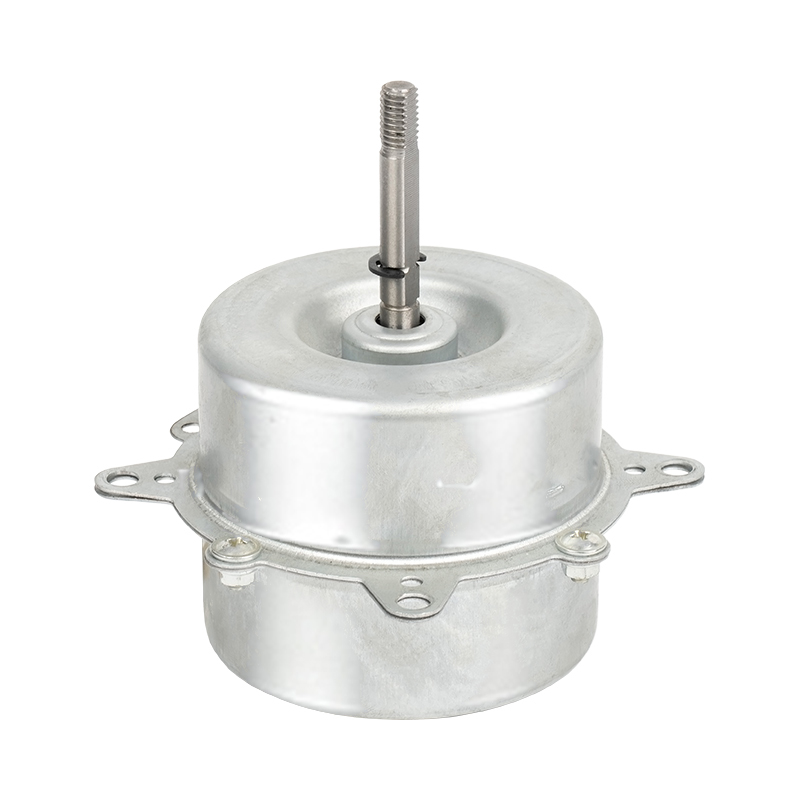
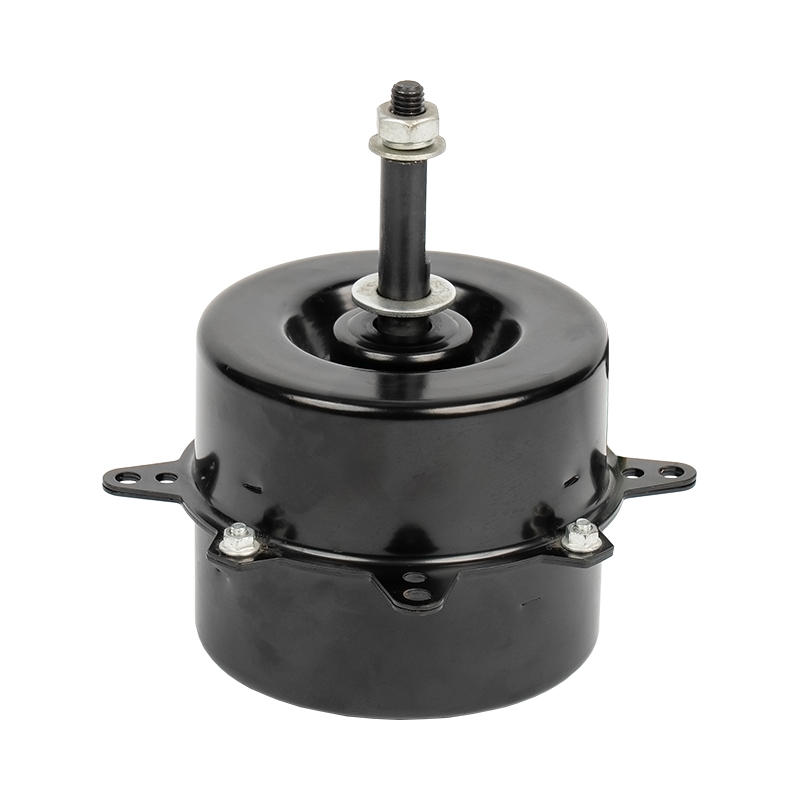
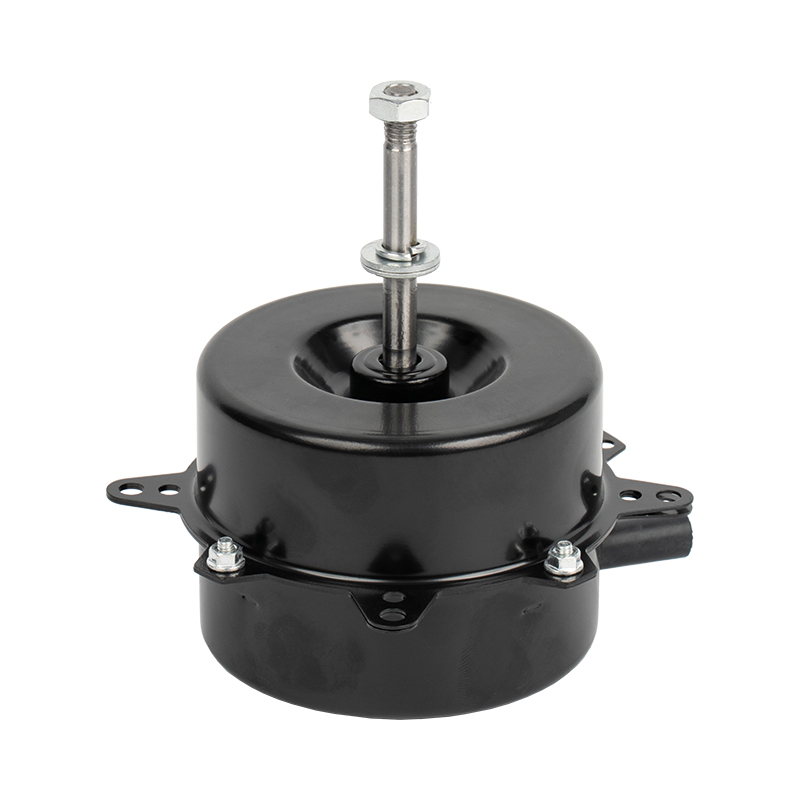















 Hogar
Hogar  +86-13968277871
+86-13968277871